- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Total Hip Replacement

Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. The main indication for total hip replacement is arthritis.
Minimally Invasive Direct Anterior Hip Replacement
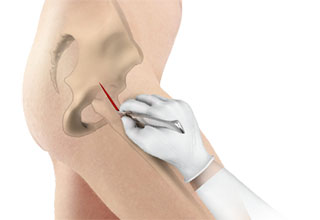
Direct anterior hip replacement is a minimally invasive hip surgery to replace the hip joint without cutting through any muscles or tendons as against traditional hip replacement that involves cutting major muscles to access the hip joint.
Revision Hip Replacement
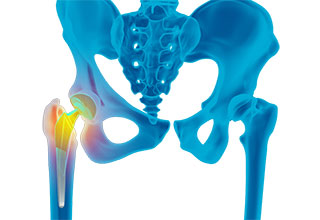
Revision hip replacement is a complex surgical procedure in which all or part of a previously implanted hip joint is replaced with a new artificial hip joint. Total hip replacement surgery is an option to relieve severe arthritis pain that limits your daily activities.
Birmingham Hip Resurfacing

The Birmingham hip resurfacing (BHR) is a metal-on-metal prosthesis used in hip resurfacing procedure. It offers a bone conserving, less invasive alternative to total hip replacement, with the potential for higher levels of normal activity. It is suitable for both young and old patients including those above 60 years, athletes, and sportsmen, and helps them lead an active life.
Hip Resurfacing
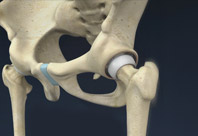
The hip joint is also known as a ball and socket joint, where the ball (femoral head) of the thigh bone fits into the socket (acetabulum) of the pelvic bone. Damage to the hip bones can be treated by hip resurfacing, which is a surgical procedure in which the damaged parts of the femoral head are trimmed, and the socket is removed and replaced with metal caps.
Hip Fracture Surgery

Hip fracture surgery is performed under anesthesia either arthroscopically or through open surgery. Your surgeon will decide which approach is the best for your condition.
Muscle Sparing Anterior Hip Replacement

Muscle sparing anterior hip replacement is a minimally invasive hip surgery to replace the hip joint without cutting through any muscles or tendons as compared to traditional hip replacement that involves cutting major muscles to access the hip joint.
Computer-Navigated Total Hip Replacement
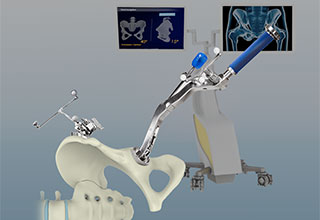
Computer-navigated total hip replacement is an advanced technology developed to provide more accurate positioning of an implant. Hip replacement through computer navigation provides information and guidance to the surgeon for precise positioning of implants.
X-ray Guided Hip Replacement
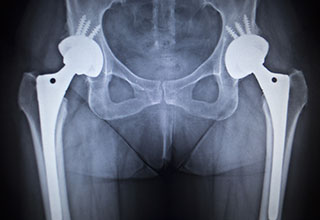
X-ray guided hip replacement involves the use of pre-operative radiographic studies to help select the right size of the implant and to determine the proper position in which the implant should be placed.
Hip Labral Repair
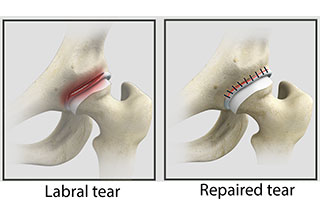
Labrum is a ring of strong fibrocartilaginous tissue lining around the socket of the hip joint. Labrum serves many functions where it acts as a shock absorber, lubricates the joint, and distributes the pressure equally.
Outpatient Hip Replacement

Hip replacement surgery is one of the most common orthopedic surgeries performed. It involves the replacement of the damaged hip bone (ball shaped upper end of the femur) with a ceramic ball attached to a metal stem that is fixed into the femur and placing a new cup with a special liner in the pelvis.

